Difference between revisions of "Graphical User Interface"
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
:This visualization comes in handy if your data is highly regular. It displays all nodes in a table with rows and columns. Different assignments can be chosen by clicking on the arrow in the right upper corner. | :This visualization comes in handy if your data is highly regular. It displays all nodes in a table with rows and columns. Different assignments can be chosen by clicking on the arrow in the right upper corner. | ||
</td></tr><tr><td valign="top"> | </td></tr><tr><td valign="top"> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Explorer.png|thumb|Explorer View]] |
'''Explorer''' | '''Explorer''' | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 29 August 2014
This page is part of the Getting Started Section. The BaseX homepage gives you a visual impression of the graphical user interface (GUI) of BaseX, and the introductory video presents some of the interactive features that the BaseX GUI provides.
Contents
Startup
First of all, please launch a GUI instance of BaseX. Depending on your operating system, double click on the BaseX GUI start icon or run the basexgui script. Beside that, some more startup options are available.
Create Database
Select Database → New and browse to an XML document of your choice. As an example, you can start with the factbook.xml document, which contains statistical information on the worlds' countries. It is included in our official releases and can also be downloaded (1.3 MB). If you type nothing in the input field, an empty database will be created. Next, choose the OK button, and BaseX will create a database that you can visually explore and query.
If no XML document is available, the Text Editor can also be used to create an initial XML document. After saving the entered XML document to harddisk, it can be specified in the above dialog.
Realtime Options
Via the Options menu, you can change how queries are executed and visualized:
- Realtime Execution: If realtime execution is enabled, your searches and queries will be executed with each key click and the results will be instantly shown.
- Realtime Filtering: If enabled, all visualizations will be limited to the actual results in realtime. If this feature is disabled, the query results are highlighted in the visualizations and can be explicitly filtered with the 'Filter' button.
Querying
Keyword Search
The Keyword Search can be executed in the Search mode in the combo box of the main window. This options allows for a simple, keyword-based search in the opened database.
The following syntax is supported:
| Query | Description |
|---|---|
world
|
Find tags and texts containing world
|
=world
|
Find exact matching text nodes |
~world
|
Find text nodes similar to world
|
@world
|
Find attributes and attribute values |
@=world
|
Find exact attribute values |
"united world"
|
Find tags and texts containing the phrase "united world"
|
XPath/XQuery
Apart from the basic search facilities, BaseX offers far more sophisticated processing options to query your documents. Below are some examples you might give a try. This guide is far from being a comprehensive XQuery reference, but might point you in the right direction.
To execute the following queries, enter them in the XQuery Panel and press ENTER or click on the START button.
XPath provides an easy facility to query your documents in a navigational manner. It is the basic tool of all node-related operations that you encounter when using XQuery. We will start with a trivial example and extend it to our needs.
Example: Find Countries
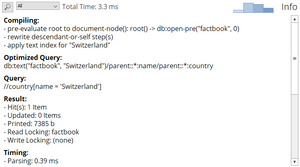
//country
tells BaseX to look for all country elements in the document. The query is introduced by two slashes //, which trigger the traversal of all document nodes. The queries //country andd /descendant::country will return the same results.
Example: Find Cities in Switzerland
The following query uses a predicate [...] to filter all country nodes which have a name child, the string value of which is "Switzerland":
//country[name = "Switzerland"]
To return all cities of the resulting element node, the query can be extended by a trailing //city path:
//country[name = "Switzerland"]//city
Text Editor
The text editor can be used to type in XQuery expressions, Command Scripts, XML documents, or any other text files. Query files and XML documents can be started by clicking on the green triangle. They will automatically parsed with each key click, and errors will be highlighted. Various keyboard shortcuts are available to speed up editing and debugging.
Visualizations
The BaseX GUI offers various visualizations, which help you to explore your XML data instances from different perspectives:
|
File:TextView.jpg Text View Text
|
File:MapView.jpg Map View Map
|
|
File:TreeView.jpg Tree View Tree
|
File:FolderView.jpg Folder View Folder
|
|
File:Scatterplot.jpg Scatterplot View Plot
|
Table
|
|
Explorer
|
Info
|
What’s Next?
Various tutorials on XPath are available in the internet. We invite you to e.g. have a look at the XQuery Tutorial at W3Schools.