Difference between revisions of "Android"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The first step is to create an Android library project, which will be later modified to represent the BaseX Android library.<br> | The first step is to create an Android library project, which will be later modified to represent the BaseX Android library.<br> | ||
In Android Studio the 'Create New Project' menu item needs to be chosen. In order to this the displayed window appears. | In Android Studio the 'Create New Project' menu item needs to be chosen. In order to this the displayed window appears. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
[[File:android-studio-new-project-dialog.png]] | [[File:android-studio-new-project-dialog.png]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
It is important that the minimum Android version is Gingerbread 2.3.3, because of some String methods used in BaseX which are not supported by Android versions older than Gingerbread. | It is important that the minimum Android version is Gingerbread 2.3.3, because of some String methods used in BaseX which are not supported by Android versions older than Gingerbread. | ||
To create an Android library project, the 'Mark this project as library' item need to be checked. An Android library is not executable and therefore does not need the creation of an Activity, which is the reason why this item is unchecked in the picture above.<br> | To create an Android library project, the 'Mark this project as library' item need to be checked. An Android library is not executable and therefore does not need the creation of an Activity, which is the reason why this item is unchecked in the picture above.<br> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
After successfully copying the corresponding BaseX packages and java files into the created Android library project a few adjustments have to be done in order to get a working Android library. | After successfully copying the corresponding BaseX packages and java files into the created Android library project a few adjustments have to be done in order to get a working Android library. | ||
At this moment the BaseX source code is presented in the Android library project as well as an empty android package, as it is shown in the following image. | At this moment the BaseX source code is presented in the Android library project as well as an empty android package, as it is shown in the following image. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
[[File:library-project-after-copying.png]] | [[File:library-project-after-copying.png]] | ||
| − | In the empty android package a new Java class needs to be created, this class is used to create the necessary BaseX files and communicate with BaseX.< | + | <br> |
| + | In the empty android package a new Java class needs to be created, this class is used to create the necessary BaseX files and communicate with BaseX. This class needs the data directory of the application for storing the corresponding BaseX files. This files should be stored in the apps /data/data/.. folder which is only accessible from the application. | ||
| + | This information is only available inside the applications context and not inside a library project, therefore it is neccessary to pass this information to this class at the constructor call. | ||
| + | The following source code shows a minimal example for a BaseX class. | ||
| + | '''Example:''' | ||
| + | <pre class="brush:java"> | ||
| + | public class BaseXDatabase { | ||
| + | private Context basexContext = null; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public BaseXDatabase(String data_dir) { | ||
| + | basexContext = new Context(data_dir); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | This class can be called in every Android application which uses the BaseX library with the following call, for example: | ||
| + | <pre class="brush:java"> | ||
| + | BaseXDatabase baseXDatabase = new BaseXDatabase(getApplicationInfo().dataDir); | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 10 April 2014
It is possible to create an Android port of BaseX. Therefore the present tutorial outlines the creation of a BaseX Android library, which can be used in any other application project. For the creation of the library the IDE Android Studio[1] is used, but the steps are more or less equal in the IDE Eclipse.
Creating the Android Library Project
The first step is to create an Android library project, which will be later modified to represent the BaseX Android library.
In Android Studio the 'Create New Project' menu item needs to be chosen. In order to this the displayed window appears.

It is important that the minimum Android version is Gingerbread 2.3.3, because of some String methods used in BaseX which are not supported by Android versions older than Gingerbread.
To create an Android library project, the 'Mark this project as library' item need to be checked. An Android library is not executable and therefore does not need the creation of an Activity, which is the reason why this item is unchecked in the picture above.
After finishing the dialog Android Studio creates an empty library project with all needed folders and files.
The next step is to copy the BaseX code into the created project folder 'src/main/java'.
Except the package 'gui' and the Java file 'BaseXGui.java' inside the 'src.main.java.org.basex'[2] package can be copied into the project folder. Android does not support Java AWT and Swing, which is the reason for not copying the gui package.
Adjusting the Code
After successfully copying the corresponding BaseX packages and java files into the created Android library project a few adjustments have to be done in order to get a working Android library.
At this moment the BaseX source code is presented in the Android library project as well as an empty android package, as it is shown in the following image.
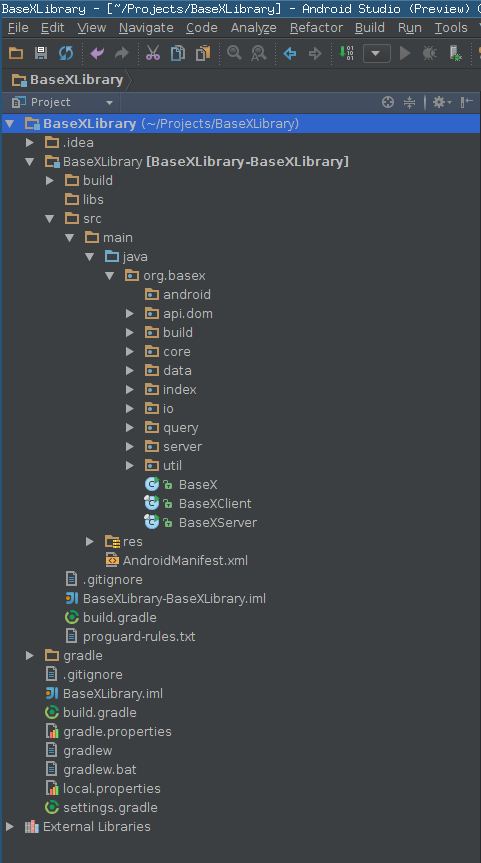
In the empty android package a new Java class needs to be created, this class is used to create the necessary BaseX files and communicate with BaseX. This class needs the data directory of the application for storing the corresponding BaseX files. This files should be stored in the apps /data/data/.. folder which is only accessible from the application.
This information is only available inside the applications context and not inside a library project, therefore it is neccessary to pass this information to this class at the constructor call.
The following source code shows a minimal example for a BaseX class.
Example:
public class BaseXDatabase {
private Context basexContext = null;
public BaseXDatabase(String data_dir) {
basexContext = new Context(data_dir);
}
}
This class can be called in every Android application which uses the BaseX library with the following call, for example:
BaseXDatabase baseXDatabase = new BaseXDatabase(getApplicationInfo().dataDir);